by Jessie Koerner
Share
Share

Summary of Innovating Sustainability: A Blueprint for Carbon-Smart Beef Production
Introduction
EcoBalance Global’s “Innovating Sustainability” project represents a significant advancement in sustainable agriculture, focusing on creating EcoSmart beef through innovative carbon management and regenerative grazing practices. This proof of concept was executed at the Open A Angus Ranch, strategically located at the border of North Dakota and Montana. Commencing in 2022, the project involved 108 cattle, meticulously tracked from birth using advanced GPS ear tags. This initiative aimed to integrate soil carbon storage into the beef supply chain, creating a new benchmark for product quality and sustainability.
Core Outcomes
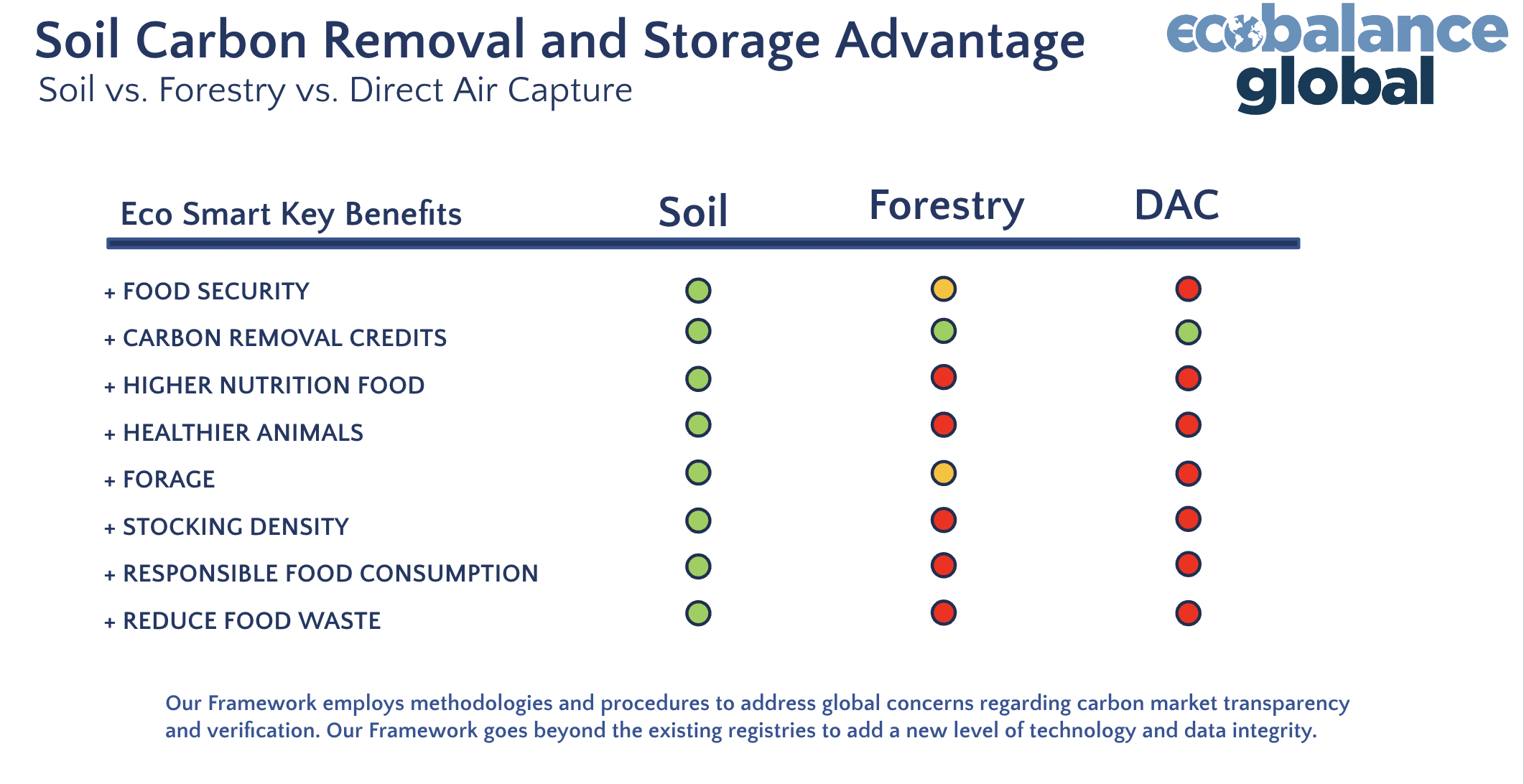
- Creation of EcoSmart Beef: The project developed a comprehensive framework integrating soil carbon storage, producing EcoSmart beef that meets high environmental standards. This achievement sets a new industry benchmark for product quality and sustainability.
- Foundation for Carbon Credit and Risk Management: The project demonstrated the capability to develop, track, and manage carbon credits within the beef supply chain. This foundation is critical for expanding EcoBalance Global’s reach into other commodities and enhancing carbon credit-risk management strategies.
- Regenerative Grazing and Enhanced Soil Carbon Storage: Implementing regenerative grazing plans crafted by expert land managers and soil scientists significantly improved soil health. These practices increased organic carbon in the soil, enhancing land resilience and sustainability.
- Robust Tracking and Verification System: Utilizing cutting-edge geospatial AI and blockchain technology, the project ensured precise tracking and third-party verification of carbon credits and beef products. This system guarantees the integrity of product claims, providing transparency and confidence to consumers and stakeholders.
Project Overview
The project timeline includes several key milestones:
2019-2022: Ranch evaluation and planning.
2022: Implementation of biologically enhanced grazing.
October 2022: Initial soil sampling to establish baseline data.
March 2023: First issuance of soil carbon credits.
October 2023: Extended soil sampling for comprehensive analysis.
November 2023: Cattle transitioned to the feedlot.
March 2024: Second round of soil carbon credits issued.
April 2024: Showcase of EcoSmart beef at the Taste of Vail event and international distribution.
Framework for Soil Carbon Storage Certification
The certification framework involves several steps:
- Project Start: Creation of a grazing management plan, initial soil sampling, and application for carbon credits.
- Follow-Ups: Regular reviews and updates of grazing practices, documentation, and reporting to the carbon credit registry.
- Re-sampling and Restart: At the end of a 5-year cycle, re-sampling of soil to assess changes in soil carbon stock and restart the cycle for continuous improvement.
Results and Analysis
- Grazing Management: Implementing Adaptive Multi-Paddock (AMP) grazing practices showed promising improvements in soil health and cattle well-being. A grazing index score was developed to objectively quantify the performance of these practices, achieving a high score and indicating significant ecological enhancement.
- Soil Carbon Baseline: Rigorous soil sampling revealed substantial increases in soil organic carbon levels, fulfilling statistical requirements for carbon credit issuance. Satellite-derived NDVI data also demonstrated marked improvements in vegetative cover, supporting the success of AMP grazing practices.
- Supply Chain Tracing and Insetting: The EcoSmart Enterprise platform enabled robust tracing of cattle and carbon credits through the supply chain, allowing for the insetting of emissions for products. This ensures transparency and efficiency in managing carbon credits and risks.
Benefits and Implications
- Direct Benefits: Improved soil health, generation of carbon credits, enhanced operational efficiency, higher quality beef, and cost savings.
- Strategic Implications: Market differentiation, policy influence, investor attraction, and industry benchmarking.
- Potential for Scaling: Replicability of the framework, wider adoption of technology, expansion of carbon markets, and collaborative partnerships.
Challenges and Lessons Learned
- Challenges: Industry fragmentation, resistance to technology, high cost of soil sampling, lack of unified data, and deficiency of robust frameworks.
- Solutions: Supply chain integration, technology implementation, third-party verification, stakeholder engagement, and flexible framework development.
- Lessons Learned: Importance of data, demand for transparency, critical role of methodology selection, value of practical experience, scalability, and economic incentives.
Conclusion
EcoBalance Global’s proof of concept at the Open A Angus Ranch demonstrates the potential of regenerative grazing practices to enhance soil health and increase soil organic carbon levels. The success of this project lays a robust foundation for expanding these practices across other commodities, promoting sustainability and profitability in unison. The call to action invites stakeholders to join in scaling these transformative solutions, contributing to a sustainable future for agriculture.